Upcoming SODIUM Hard Fork: a New Milestone for Burstcoin

The open-source Burstcoin blockchain was first developed in 2014 and has been at the forefront of blockchain technology with the first implementation of smart contracts. Burst is the pioneer of the “Proof Of Capacity” consensus algorithm, a green alternative to Proof of Work. Right now, it is preparing for a new milestone in the evolution of its blockchain with the upcoming SODIUM hard fork.
What is the SODIUM Hard Fork all about?
The Burstcoin Reference Software (BRS) version 2.5.0 was released on 10 May 2020 and included all the protocol changes which will be activated at blockheight 765,000 (around 20 June 2020). It is recommended that all Bursters update their respective nodes to get all the benefits of the updated software. When BRS 2.5.0 activates the hard fork, all nodes with a version lower than 2.5.0 will be abandoned from the Burstcoin mainnet.
The hard fork contains a set of modifications to the Burst protocol which are described in the CIP overview (CIP20, CIP22 to CIP25). While the API updates detailed in CIP22 contains no breaking changes, these changes will expand the ability for miners and nodes to operate within the network.
Blocktime Stabilization (CIP23)
The current implementation in Burstcoin, the pioneer of Proof of Capacity, results in very good block time averages, with daily deviations smaller than 5% around the target value of 4 minutes (240 seconds). The individual block times, on the other hand, show a broad deviation with block times typically ranging from 10 seconds to 2000 seconds (30 minutes). With this protocol change, a reduction of individual block times variation is proposed.
This will create an environment of stable blocktimes around 240 seconds which can be trusted by businesses and related DApps and creates a better user experience.
Smart Contract Upgrade (CIP20)
A smart contract is a computer protocol intended to digitally facilitate, verify, or enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract. Smart contracts are computer programs that automatically execute the terms of a contract on the blockchain and allow the performance of credible transactions without third parties. These transactions are trackable and irreversible.
Smart contracts (also known as Automated Transactions) have become an increasingly important feature for next-generation financial technology. The Burstcoin blockchain now has the ability to run larger and more complex smart contracts with lower fees. Combined with the BlockTalk Java smart contract compiler, these changes bring the creation of new trustless projects (DeFi, Non-Fungible Tokens, DEXs, Games, etc), which were before unimaginable, within reach.
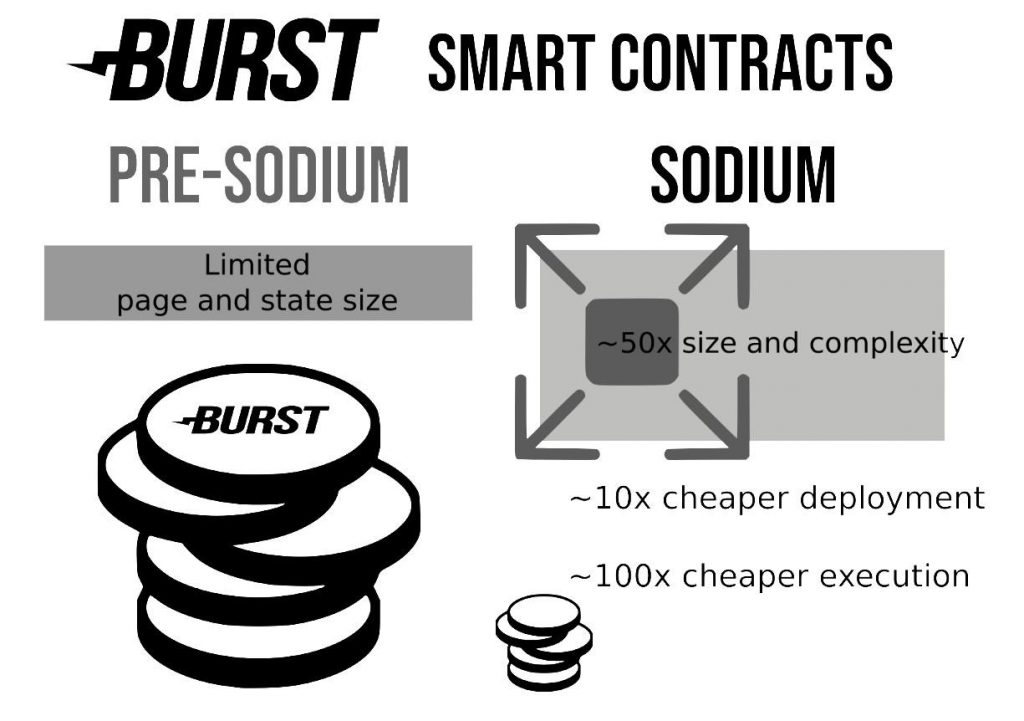
The benefits that will be seen in smart contracts due to the release of these new protocols are increased complexity and decreased cost. The updated smart contracts can manage a 50x higher complexity and have 10 times cheaper execution cost.
Fee Slot Enforcement (CIP23)
In relation to CIP03, the slot-based transaction fee system allows for variable fees depending on the transaction load on the blockchain. As a secondary goal, it prevents spamming blocks with lots of transactions with minimum fees. However, the block validation did not strictly enforce these minimum fees used relative to the slot number.
With this protocol change enabled, validating a block will check the fee amounts of all transactions to ensure these fees conform to the minimum. Otherwise the block will be deemed invalid. This change also implies the removal of fat forging blocks where all fees are disregarded. This caused an unenforceable and unbalanced distribution of fees among the blocks and their miners.
Burst Deep Link Specification (CIP22)
The sole purpose of the deep linking feature is to streamline the use of various applications of the platform. For example, the use of the messaging application, wallet application, token exchange application can be made individually while keeping them in the same integrated system or platform. The new feature can also be used to create meta applications.
Subscription Fee Reduction + Minor Network Changes (CIP25)
When the new fee model was introduced with CIP03, the execution costs of a subscription were not adjusted. The fees for subscriptions still remained at 1 Burst per subscription payment. This change makes the fee for a subscription payment 0.00735 Burst. Also, minor security changes are introduced to the blockchain network with this protocol change.
BRS 3.0 is coming!
After the hard fork of BRS 2.5.0 and the implementation of all the protocol changes on the blockchain network, BRS 3.0 will be released (second half of 2020). This will bring further enhancements to the Burst Reference Software like:
Java to Kotlin
Unlike the older version, the new BRS 3.0 is written in Kotlin that will make it compatible with almost every platform or hardware. This will open a window of endless possibilities. Moreover, the speed and efficiency of BRS 3.0 will be greatly increased compared to previous versions.
UI Overhaul
Phoenix, an open-source cross-platform Burst Wallet UI, will be the default wallet UI in BRS 3.0. Phoenix provides multiple account management, improved security, and better interoperability. Phoenix makes it very easy to integrate Burstcoin in projects and webshops for quick and easy payments. For users who still want to use the legacy UI, a link will be provided to it, which will ship alongside Phoenix in BRS 3.0.

Performance Improvements
BRS 3.0 is much faster and more efficient than prior BRS versions. Running a BRS 3.0 node will be easier and more energy-efficient than ever before. BRS 3.0 represents years of hard work toward the vision of making Burstcoin even more green, while staying truly decentralized.
Summary of the SODIUM hard fork
- On May 10 2020, BRS 2.5 (Java) was released.
- Around 20 June 2020, the Burst blockchain will hard fork at block 765,000.
- Includes improvements CIP 20, 22, 23, 24 and 25.
- In the second half of 2020, BRS 3.0 (a Kotlin rewrite) will be released.
SODIUM is supported by BMF (Burst Marketing Fund) and BTDEX (BlockTalk Decentralized Exchange). Also, the NDS-A (a reward for full-node operators) is already updated to check for BRS 2.5.0 full nodes before distributing rewards.
Final Words
BRS 2.5.0 and 3.0 together represent over a year’s worth of work by the Burst Apps Team (BAT) in collaboration with the community. Through rigorous testing, reviews, and iterations, the Burst Apps Team has been preparing for this event for months. They are proud of the results, and are excited to work with the community on the successful deployment of this and future hard forks.
References
SODIUM Hard Fork: Technical Details
All Aboard the SODIUM Hard Fork
